| [1] 牛忠英,裴振华,施生根,等.慢性牙周炎患者粘接性牙周夹板固定修复的临床应用研究[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志, 2012,13(4):193-197.[2] 李显峰,陈倩,王晓静,等.龈沟液成分在牙周病和冠修复中的临床意义[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志, 2010,8(2):124-126.[3] Polzer K,Joosten L,Gasser J,et al.Interleukin-1 is essential for systemic inflammatory bone loss.Ann Rh eum Dis.2010;69(1):284-290.[4] 唐震宇,汪海峰,蒋颍泉,等.非贵金属合金材料钴铬合金烤瓷联冠式固定夹板用于牙周炎修复[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(25):4889-4892.[5] 姚远.烤瓷牙夹板修复老年牙周病患牙的临床分析[J].贵阳中医学院学报,2014,36(3):81-82.[6] 李征,崔杰,王星,等.烤瓷夹板联合植骨修复牙周骨缺损基牙牙周的变化[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(34): 6103-6109.[7] 谭学东,符光鹏,黄丹,等.烤瓷牙夹板修复老年牙周病患牙效果分析[J].吉林医学,2012,33(13):2747-2748.[8] 许力强,王毅,李晓宇.采用套筒冠义齿修复牙周病伴牙列缺损的临床研究[J].齐齐哈尔医学院学报, 2010,31(12): 1894-1895.[9] 王莹,王慧敏,郭丹.浅析牙周病修复治疗的依据[J].中外健康文摘,2011,8(48):169-170.[10] Nevins M,Kim DM.Classical versus contemporary treatment planning for aggressive periodontal disease. J Periodontol.2010;81(5):767-775.[11] 关雅梅.金属烤瓷联冠在慢性牙周病治疗中的体会[J].中外健康文摘,2011,8(8):388.[12] 刘志利,王暐.可摘式钛合金牙周夹板治疗松动牙的疗效观察[J].海南医学院学报,2012,18(5):687-688,691.[13] Rajan G,Baig MR,Nesan J,et al.Fixed rehabilitation of patient with aggressive periodontitis using zygoma implants.Indian J Dent Res.2010;21(1):125-128.[14] Levin L,Ofec R,Grossmann Y,et al.Periodontal disease as a risk for dental implant failure over time:a long-term historical cohort stud.J Clin Perio dontol. 2011;38(8): 732-737.[15] 施斌.牙周病致后牙区牙槽骨严重吸收的种植义齿修复[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2011,46(11):665-668.[16] Vigolo P,Zaccaria M.Clinical evaluation of marginal bone level change of multiple adjacent implants restored with splinted and nonsplinted restorations: a 5-year prospective study.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2010;25(6):1189-1194.[17] 祝红伟.精密附着体技术的临床应用研究[J].中外健康文摘,2011,8(4):33-34.[18] Boas Nogueira AV,Chaves de Souza JA,Kim YJ.Orthodontic force increases interleukin-1β and tumor necrosis factor-α expression and alveolar bone loss in periodontitis.J Periodontol. 2013;84(9):1319-1326.[19] 安涓,薛雯,赵献平,等.磁性附着体在牙周病牙列缺损修复治疗中的应用体会[J].中外健康文摘,2012,9(7):29-30.[20] 谢静忠.牙周病骨质缺损的正畸牵引成骨治疗[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2010,26(5):690-691.[21] Gkantidis N,Christou P,Topouzelis N.The orthodontic—periodontic interrelationship in integrated treatment challenges: a systematic review. J Oral Rehabil. 2010;37(5):377-390.[22] 吴艳,伏艳,米方林,等.成人牙周炎患者正畸治疗前后TNF-α含量的变化[J].临床口腔医学杂志, 2012,28(7): 400-402.[23] 钱文慧,徐艳,孙颖,等.富血小板血浆修复牙周骨缺损的临床疗效[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2014,24(7):415-418.[24] 张月兰,时毅,刘林嶓,等.正畸力大小对牙周健康成人牙齿移动速度的影响[J].河南医学研究, 2012,21(3):280-282, 284.[25] Roshna T,Nandakumar K.Generalized aggressive periodontitis and its treatment options: case reports and review of the literature.Case Rep Med. 2012;2012: 535321.[26] 殷艳丽,王倩婷,赵蕾.脱细胞真皮基质用于牙周病学领域研究进展[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2014,7(7):434-439.[27] Joshi NV.Periodontal status following treatment of impacted maxillary canines by closed e ruption technique: an overview and case report.Compend Contin Educ Dent.2014;35(3):12-17.[28] Dinoi MT,Lacarbonara M,Dimartino S,et al.Periodontal probing of an impacted tooth recovered through a surgical- orthodontic approach: a case report.J Med Case Reports.2014;35(8):106-116.[29] 顾媛媛.30例牙周病修复治疗的临床体会[J].大家健康:下旬刊,2013,7(9):105-106.[30] 蔡同道.盐酸米诺环素软膏治疗种植体周围炎的疗效观察[J].中国医药科学,2012,2(11):168,170.[31] Ghijselings E,Coucke W,Verdonck A,et al.Long -term changes in microbiology and clinical periodontal variables after completion of fixed orthodontic appliances. Orthod Craniofac Res.2014;17(1):49-59.[32] 周洁,张敏,李琳,等.正畸-牙周联合治疗成人牙周病伴错牙合畸形[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志, 2012,22(9):517, 528-530.[33] 杨艳,范繁,邓岚,等.八珍汤加减对牙周炎大鼠正畸移动的影响[J].武汉大学学报:医学版,2012,33(5):656-659,666.[34] 贾英民,武密山,李恩,等.补肾方剂对成骨细胞体外培养干预的研究进展[J].现代中西医结合杂志, 2011,20(31): 4035-4037.[35] 胡骁颖,董福生,袁硕,等.补肾方剂对骨质疏松伴牙周炎家兔正畸牙移动中牙周组织作用的组织学观察[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2012,28(4):426-429.[36] Koromantzos PA,Makrilakis K,Dereka X,et al.A randomized,controlled trial on the effect of nonsurgical periodontal therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes. PartⅠ: effect on periodontal status and glycaemic control.J Clin Periodontol.2011;38(2):142-147.[37] 杨东红,王石,吴立鹏.牙周炎正畸牙周组织中胰岛素样生长因子-Ⅰ表达的实验研究[J]. 现代口腔医学杂志, 2012, 26(4):262-265.[38] Hazan-Molina H,Levin L,Einy S,et al.Aggressive periodontitis diagnosed during or before orthodontic treatment.Acta Odontol Scand.2013;71(5):1023-1031.[39] 钱雅婧,钟良军,米丛波.正畸力作用下大鼠炎性牙周组织改建及白细胞介素6的表达[J].中华口腔医学研究杂志, 2010,4(5):447-455.[40] Sanikop S,Patil S,Agrawal P.Gingival crevicular fluid alkaline phosphatase as a potential diagnostic marker of periodontal disease.Indian Soc Periodontol. 2012; 16(4): 513-518. |
.jpg)
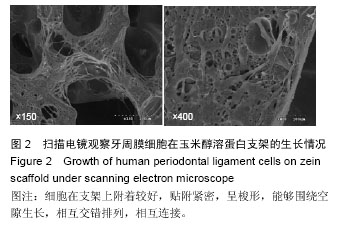
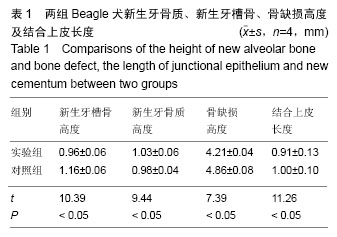
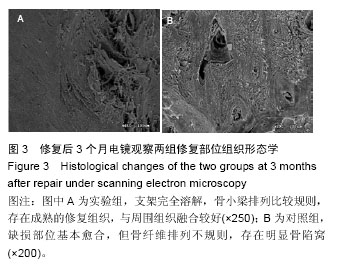
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)